- HHD
- Wuhan Hubei
custom synthesis
 diAcCA, a Pro-Drug for Carnosic Acid That Activates the Nrf2 Transcriptional Pathway, Shows Efficacy in the 5xFAD Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease
diAcCA, a Pro-Drug for Carnosic Acid That Activates the Nrf2 Transcriptional Pathway, Shows Efficacy in the 5xFAD Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease

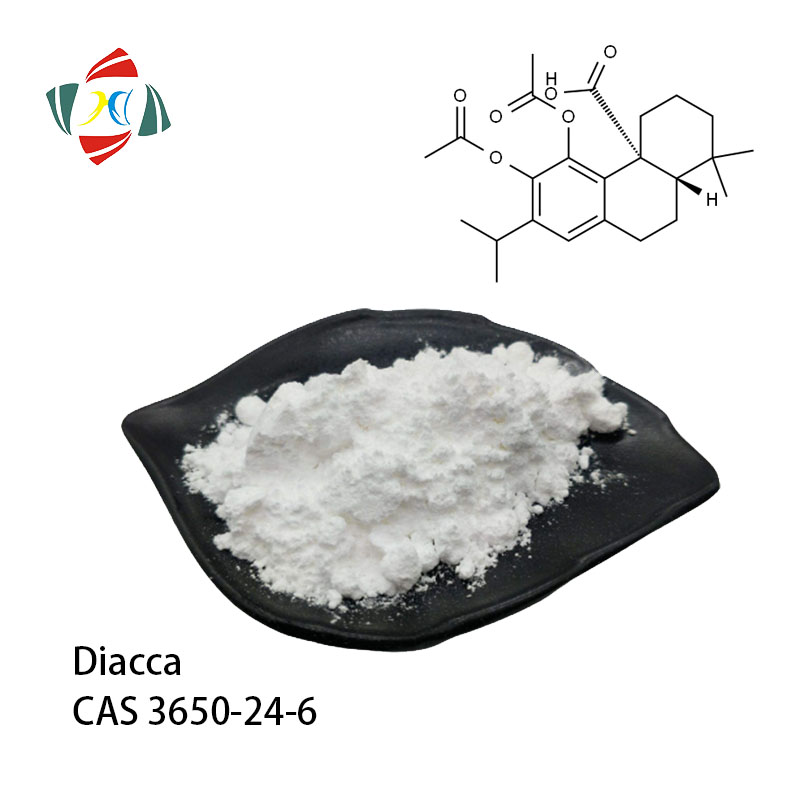
Product Name | diAcCA/di-acetylated carnosic acid |
Brand | HHD |
CAS No. | 3650-24-6 |
Appearance | off-white powder |
Purity | min 98% |

diAcCA, or di-acetylated carnosic acid, is a newly developed, stabilized derivative of carnosic acid, an antioxidant found in rosemary and sage. It is being investigated as a potential treatment for Alzheimer's disease because it showed promise in early-stage mouse studies by improving memory, reducing brain inflammation, and clearing toxic proteins linked to the disease.

Mechanism of Action: diAcCA works primarily by activating the Nrf2 transcriptional pathway, which is the body's natural defense system against oxidative stress and inflammation. It also appears to reduce the formation of amyloid plaques and tau tangles, key biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease.
Stability and Bioavailability: Pure carnosic acid (CA) is highly unstable, which limits its use as a drug. Scientists at Scripps Research developed diAcCA as a more stable derivative with a shelf life of over two years. When ingested, diAcCA is efficiently converted to CA in the stomach and absorbed into the bloodstream, achieving better bioavailability and higher brain levels of CA than taking CA directly.
Research Findings (Preclinical): In studies using mouse models of Alzheimer's disease, oral administration of diAcCA for three months led to:
Significant improvements in memory and learning.
Increased synaptic density (connections between nerve cells).
Reduced neuroinflammation and microglial activation.
Decreased levels of toxic amyloid-beta and phosphorylated-tau proteins.
Memory function improved "virtually back to normal" in treated mice.
Clinical Potential: The researchers are optimistic about advancing diAcCA to human clinical trials. Because the metabolite carnosic acid has a "Generally Recognized as Safe" (GRAS) status from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the clinical trial process might be expedited.
Potential Broader Applications: Besides Alzheimer's, diAcCA's anti-inflammatory properties suggest it could have applications for other conditions marked by inflammation and oxidative stress, such as Parkinson's disease, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Every batch of our product was tested by authorized independent third party, Analysis testing center, Shanghai branch, Chinese Academy of Science. We send goods to customers with test report and COA. Our products were also tested by American Analytical Chemistry Laboratories and Chromadex too....more














